
- #Find terms in arithmetic sequence calculator how to
- #Find terms in arithmetic sequence calculator series
Their complexity is the reason that we have decided to just mention them, and to not go into detail about how to calculate them. Talking about limits is a very complex subject, and it goes beyond the scope of this calculator. It can also be used to try to define mathematically expressions that are usually undefined, such as zero divided by zero or zero to the power of zero. This is a mathematical process by which we can understand what happens at infinity. For this, we need to introduce the concept of limit.
#Find terms in arithmetic sequence calculator series
As you'll learn in the following sections, the infinite sum may not exist!Īfter seeing how to obtain the geometric series formula for a finite number of terms, it is natural (at least for mathematicians) to ask how can I compute the infinite sum of a geometric sequence? It might seem impossible to do so, but certain tricks allow us to calculate this value in a few simple steps.

In the latter case, it suffices to input the starting and final point of the sum, and you can enjoy the result. Our tool can also compute the sum of your sequence: all of it or a final portion. You can change the starting and final terms according to your needs. By default, the calculator displays the first five terms of your sequence.Based on that, the calculator determines the whole of your geometric sequence. the common ratio and some n th term or.the common ratio and the first term of the sequence.First, tell us what you know about your sequence by picking the value of the Type:.Here's a brief description of how the calculator is structured: Now that you know what a geometric sequence is and how to write one in both the recursive and explicit formula, it is time to apply your knowledge and calculate some stuff! With our tool, you can calculate all properties of geometric sequences, such as the common ratio, the initial term, the n-th last term, etc.
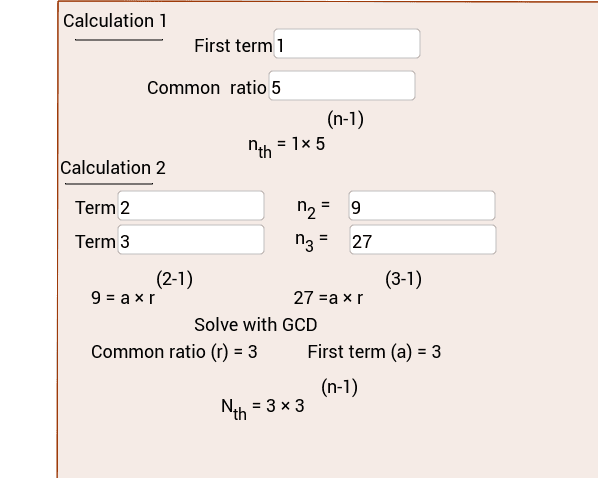
But if we consider only the numbers 6, 12, 24 the GCF would be 6 and the LCM would be 24. For example, in the sequence 3, 6, 12, 24, 48 the GCF is 3 and the LCM would be 48. Conversely, the LCM is just the biggest of the numbers in the sequence. This means that the GCF (see GCF calculator) is simply the smallest number in the sequence. Indeed, what it is related to is the [greatest common factor (GFC) and lowest common multiplier (LCM) since all the numbers share a GCF or a LCM if the first number is an integer. First of all, we need to understand that even though the geometric progression is made up by constantly multiplying numbers by a factor, this is not related to the factorial (see factorial calculator). We also include a couple of geometric sequence examples.īefore we dissect the definition properly, it's important to clarify a few things to avoid confusion. If you are struggling to understand what a geometric sequences is, don't fret! We will explain what this means in more simple terms later on, and take a look at the recursive and explicit formula for a geometric sequence. The geometric sequence definition is that a collection of numbers, in which all but the first one, are obtained by multiplying the previous one by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
